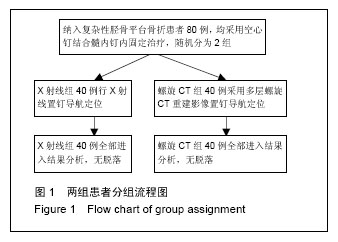
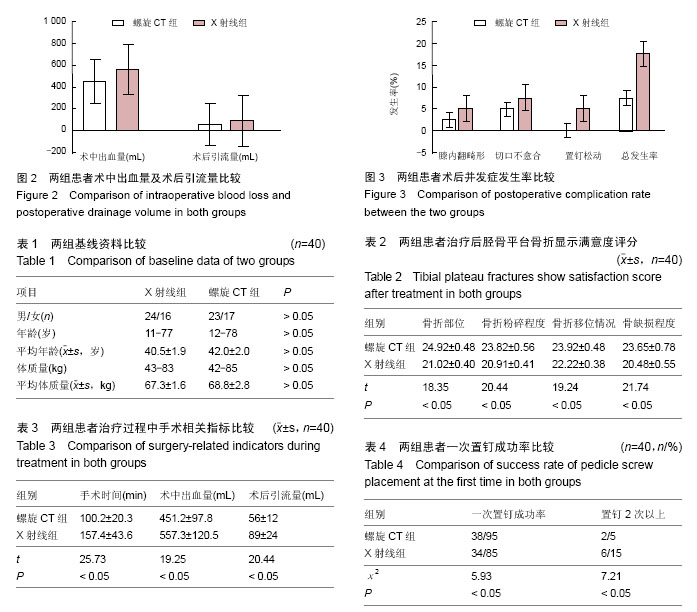
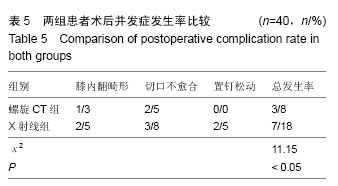
| [1] 李林,蒋亦军,邓家仁.锁定钢板内固定治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折临床疗效观察[J].海南医学院学报,2012,18(7): 932-934.
[2] 蔡伟斌,胡鸿璇,郭新辉,等.锁定加压钢板与解剖钢板置入内固定治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(52):9750-9755.
[3] 楚晓丰,阮洪江,姚束烨.关节镜辅助下微创手术治疗胫骨平台骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,23(4):374-375.
[4] Zhu Y,Yang G,Luo CF,et al.Computed tomography-based Three -Column Classification in tibial plateau fractures:introduction of its utility and assessment of its reproducibility. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(3):731-737.
[5] 刘宗超,蒋燕,杨家福,等.有限内固定结合外固定支架与钢板治疗胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(6):505-508.
[6] 巴雪峰,孙改生,凯瑟尔,等.胫骨平台骨折的治疗新进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(12):1104-1107.
[7] 袁彦成,曾军平,胡国富,等.钢板内固定治疗胫骨平台骨折42例临床分析[J].江西医药,2012,47(5):459-460.
[8] Chang SM,Zhang YQ,Yao MW,et al.Schatzker type Ⅳ medial tibial plateau fractures:a computed tomography -based morphological subclassification.Orthopedics. 2014;37(8):699-706.
[9] 冯涛.胫骨平台骨折38例关节镜及C形臂X线机微创治疗的临床研究[J].中国内镜杂志,2014,20(11):1195-1200.
[10] 张峻玮,孙磊,毕宏政,等.胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(14):1280-1283.
[11] 赵刚,和桓德,陈朝伟,等.复杂胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(20):1902-1905.
[12] Zou H,Ma X,Tang C,et al. Biomechanical study on a novel injectable calcium phosphate cement containing poly ( latic-co-glycolic acid) in repairing tibial plateau fractures.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(7): 855-859.
[13] 许振波,李强,胡敦祥,等. 三钢板内固定治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J]. 江西医药,2013,48(12):1200-1202.
[14] te Stroet MA,Holla M,Biert J. The value of a CT scan compared to plain radiographs for the classification and treatment plan in tibial plateau fractures. Emerga Radiol. 2011;18(3):279-283.
[15] 张国强,丁尔勤.胫骨平台骨折的诊疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(10):1078-1079.
[16] Yang G,Zhai Q,Zhu Y,et al.The incidence of posterior tibial plateau fracture:an investigation of 525 fractures by using a CT-based classification system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(4):929-934.
[17] 左树青,丰佳萌.64排螺旋CT后处理技术在胫骨平台骨折中的应用价值[J].中国当代医药,2013,20(12):116-117.
[18] Hu YL,Ye FG,Ji AY,et al.Three-dimensional computed tomography imaging increases the reliability of classifi-cation systems for tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2009;40(2):1282-1285.
[19] Dodd A,Oddone Paolucci E,Korley R.The effect of three- dimensional computed tomography reconstructions on preoperative planning of tibial plateau fractures:a case -control series.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(6):144-149.
[20] Ocegueda - Sosa MA,Valenzuela - Flores AA,Aldaco - Garcia VD,et al. Clinical practice guideline on closed tibial plateau fractures in adulthood. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2013;51(5):592-599.
[21] de Lima Lopes C,da Rocha Candido Filho CA,de Lima E Silva TA,et al. Importance of radiological studies by means of computed tomography for managing fractures of the tibial plateau. Rev Bras Ortop. 2014; 49(6):593 -601.
[22] 谢卫宁,杨英年,李华,等.AO/OTA 及三柱分型联合应用指导治疗累及后柱的胫骨平台骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(10):1052-1053.
[23] Patange Subba Rao SP,Lewis J,Haddad Z,et al.Three column classification and Schatzker classification:a three-and two-dimensional computed tomography characterization and analysis of tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(7):1263-1270.
[24] Wang J,Wei J,Wang M.The distinct prediction standards for radiological assessments associated with soft tissue injuries in the acute tibial plateau fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(5):913-920.
[25] 梁卫东,李世梁,宋颖军,等.胫骨平台骨折治疗策略研究进展[J].中国民族民间医药杂志,2013,22(14):43-45.
[26] 翟启麟,罗从风,朱奕,等.胫骨平台后侧骨折的诊断和治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(7):615-618.
[27] Walz M,Auerbach F,Kolbow B,et al.Minimally invasive treatment of monocondylar tibial plateau fractures. Percuta-neous reduction and small fragment osteosynthesis. Unfallchirurg. 2006;109: 367-376.
[28] 赵永强,黄遂柱.关节镜联合MIPPO技术治疗腔骨平台骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24: 1121-1122.
[29] Gicquel T,Najihi N,Vendeuvre T,et al. Tibial plateau fractures: Reproducibility of three classifications (Schatzker,AO,Duparc ) and a revised Duparc classification. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7): 805-816.
[30] Patange SR, Lewis J,Haddad Z,et al.Three-column classification and Schatzker classification: a three-and two-dimensional computed tomography characterisation and analysis of tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013.
[31] Chen WT,Zhang YQ,Chang SM. Posterolateral approach for plating of tibial plateau fractures and the risk of injury to the anterior tibial vessels. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(9): 228-229.
[32] 张绍东,姜星杰,吴小涛.三种骨水泥应用于椎体成形术的生物力学比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(3): 205-209.
[33] Bai B,Kummer FJ,Sala DA,et al. Effect of articular sfep-off and me niscectomy on joint alignment and contact pressures for fractures of the lateral tibial plateau. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15: 101-106.
[34] Jansen H,Frey SP,Doht S,et al. Medium-term results after complex intra -articular fractures of the tibial plateau. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(4):569-577.
[35] Broome B,Mauffrey C,Statton J,et al. Inflation osteoplasty:in vitro evaluation of a new technique for reducing depressed intra-articular fractures of the tibial plateau and distal radius. J Orthop Traumatol. 2012; 13(2):89-95.
[36] 仲飙,张弛,孙辉,等.后外侧联合后内侧入路治疗胫骨平台后柱骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012, 27(10):899-901.
[37] 王邦军,胡杨,严力军,等.双切口3块钢板内固定治疗 SchatzkerⅥ型胫骨平台骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(6):611-612.
[38] 陈超,梁志白.髌骨旁外侧切口双钢板内固定治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(10):939-940. |